When your motorcycle battery dies unexpectedly, especially when you’re miles from home, it can quickly turn an enjoyable ride into a stressful situation. While many riders focus on the battery itself, one often-overlooked culprit behind battery failure is the stator. This essential component of your bike’s electrical system plays a crucial role in charging your battery and keeping the bike running smoothly. Understanding how the stator works, how to identify when it’s failing, and how to replace it can save you from costly repairs and frustrating breakdowns.
Contents
What is a Stator on a Motorcycle?
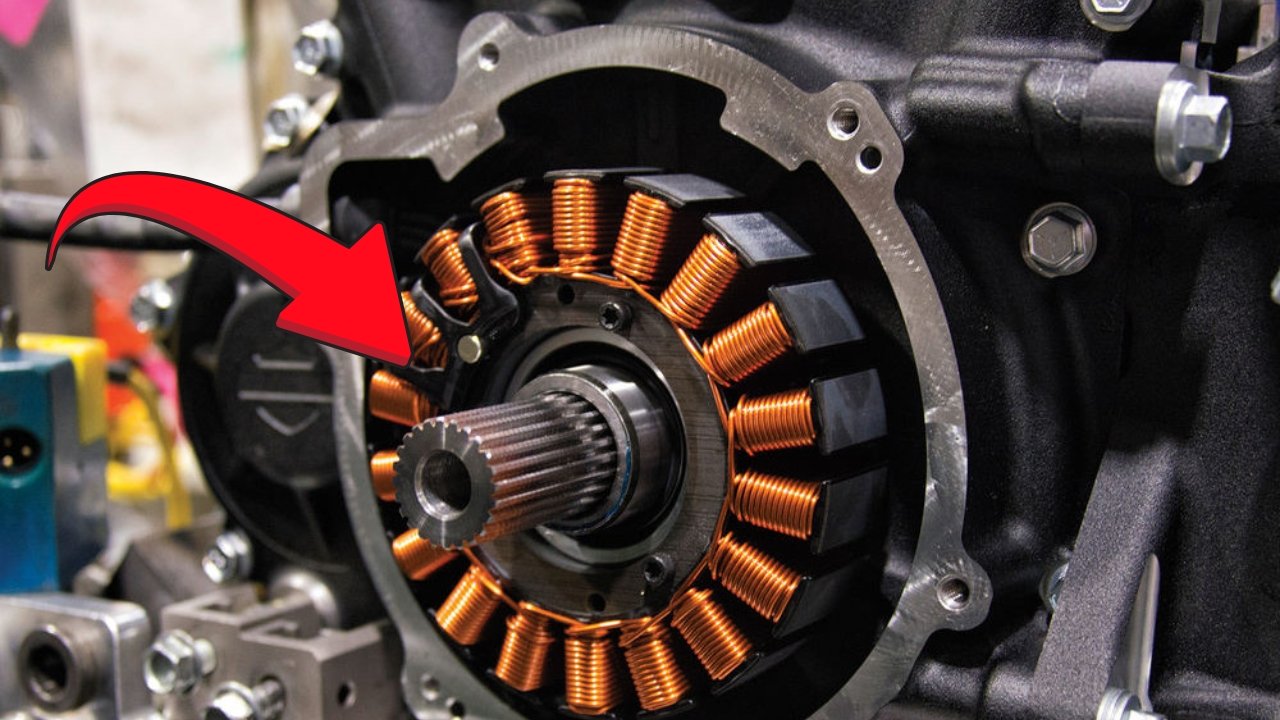
The stator is a key part of your motorcycle’s charging system, designed to generate the power needed to charge the battery and keep the bike’s electrical components functioning. Located inside the engine casing, usually near the flywheel, the stator is an integral piece of machinery that keeps your bike running by supplying electrical energy to various systems, such as the lights, ignition, and fuel pump.
Although it is generally housed within the engine casing, the exact location and design of the stator can vary depending on the make and model of the motorcycle. This system is found not just in full-sized motorcycles but also in smaller bikes and kids’ ride-on toys with petrol engines.
How Does a Stator Work?
The stator operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction, which involves the conversion of mechanical motion into electrical energy. It consists of a coil of wire that is positioned inside the engine case. The key to its function is the interaction between a rotating magnet and the coil. As the engine runs, the magnet spins within the coil, generating alternating current (AC) through a process known as Faraday’s law.
This AC power generated by the stator is then sent to a component called the rectifier/regulator. The rectifier’s job is to convert the AC into direct current (DC), which is used to charge the battery and supply power to the bike’s electrical systems. Without a properly functioning stator, the battery would quickly drain, leaving the motorcycle unable to run.
Charging the Motorcycle Battery
A properly functioning stator is crucial to keeping your battery charged. The electrical power generated by the stator not only charges the battery but also powers essential systems like the bike’s ignition, lights, and fuel pump. If the stator fails, the battery will not receive a proper charge and will deplete much faster than usual, leading to starting problems and the potential failure of other electrical components.
Signs of a Faulty Stator
Recognizing the signs of a failing stator early on can save you a lot of time and money. Common symptoms of a bad stator include:
- Starting Issues: If your motorcycle is having trouble starting, or if the battery seems to lose its charge quickly, the stator might be to blame. Without sufficient power from the stator, the bike may struggle to start, especially after sitting idle for a period.
- Dim or Flickering Lights: The stator provides power to your bike’s lights, so if you notice flickering headlights or lights that are unusually dim, it could be an indication that the stator is no longer supplying the proper amount of power.
- Frequent Battery Replacements: A bad stator can lead to rapid battery drain, which may cause the battery to fail prematurely. If you find yourself needing to replace the battery more often than expected, this could be a sign of a failing stator.
- Increased Fuel Consumption: In some cases, a malfunctioning stator can cause the engine to run inefficiently, leading to increased fuel consumption. This might not always be a noticeable symptom right away but can contribute to higher operating costs in the long run.
The Impact of a Failing Stator
A malfunctioning stator can have significant consequences for your motorcycle. As the stator fails to generate sufficient power, the battery will not charge properly. This leads to a cascade of issues, including the inability to start your bike and electrical systems failing to operate. Additionally, a bad stator can strain the engine, potentially causing further damage to other components. Over time, this can lead to expensive repairs or even engine failure if the issue is left unaddressed.
How to Test and Replace a Faulty Stator
Testing the Stator: One way to determine if your stator is failing is by using a multimeter to test its resistance and output voltage. A healthy stator will produce consistent readings, while irregular or low readings can indicate that it is faulty. If you’re not comfortable testing the stator yourself, a mechanic can perform these tests for you.
Replacing the Stator: Replacing a stator requires a bit of mechanical know-how. To replace the stator, the left-side engine cover must be removed, the old stator disconnected, and a new stator installed in its place. Reassembly is required after the new part is installed. While it’s possible for some experienced riders to perform this repair themselves, it’s generally recommended to seek professional help if you’re not familiar with engine repairs. Improper installation could lead to further issues down the road.
Can You Ride a Motorcycle Without a Stator?
It is technically possible to ride a motorcycle with a faulty stator, but only for a limited time. If the stator is not working properly, your motorcycle will quickly drain its battery, and you may find yourself stranded. Think of it like running a marathon without food: you can start strong, but eventually, you’ll run out of energy. In this case, a dead battery will bring your ride to a halt, so it’s important to replace a failing stator as soon as possible to avoid getting stuck.
Conclusion
The stator is a vital component of your motorcycle’s charging system. It ensures that your battery stays charged and powers essential systems such as lights, ignition, and the fuel pump. Regular maintenance, including testing the stator periodically and replacing it when necessary, can help avoid breakdowns and prolong the life of your motorcycle.
By understanding the function of the stator and recognizing the signs of failure early, you can prevent costly repairs and frustrating roadside incidents. A little attention to this key component can go a long way in keeping your bike running smoothly and reliably.
FAQs
What does a stator do on a motorcycle?
The stator generates electrical power that charges the battery and powers the motorcycle’s ignition, lights, and other electrical systems.
What are the signs of a bad stator?
Starting issues, dim or flickering lights, frequent battery replacements, and increased fuel consumption can all indicate a failing stator.
Can I ride with a bad stator?
Riding with a bad stator is not recommended. While you may be able to start the bike, the battery will quickly drain, leaving you stranded.
How long does a motorcycle stator typically last?
A stator can last anywhere from 7,000 to 28,000 miles, depending on usage and maintenance.
Can I use a car battery charger for a motorcycle battery drained by a bad stator?
Yes, a car battery charger can be used for a motorcycle battery, but ensure compatibility and use a low-amp setting to avoid damaging the battery.